0
You have 0 items in your cart
- Home
- Tooling & Automation
- Companies & Capabilities
- Segen Quick Change
- News
- Resources
- About Us
- Contact Us
Successful automation projects begin with our design team translating your unique needs into a practical and efficient system. As part of our comprehensive robotic automation integration and assembly solutions, our staff of seasoned multi-disciplinary engineers, including mechanical, process automation and controls experts, work across today’s CAD/CAM and simulation software to create solutions that streamline your operations.
Robotic automation is an excellent way to enhance assembly processes — helping to streamline production, increase efficiency, improve quality control, and reduce labor costs. As part of our robotic automation integration and assembly solutions, we offer automated assembly systems ranging from simple setups and lean cells involving basic machinery to highly complex systems incorporating advanced robotics, vision systems, and artificial intelligence, including solutions provided by Century Automation.
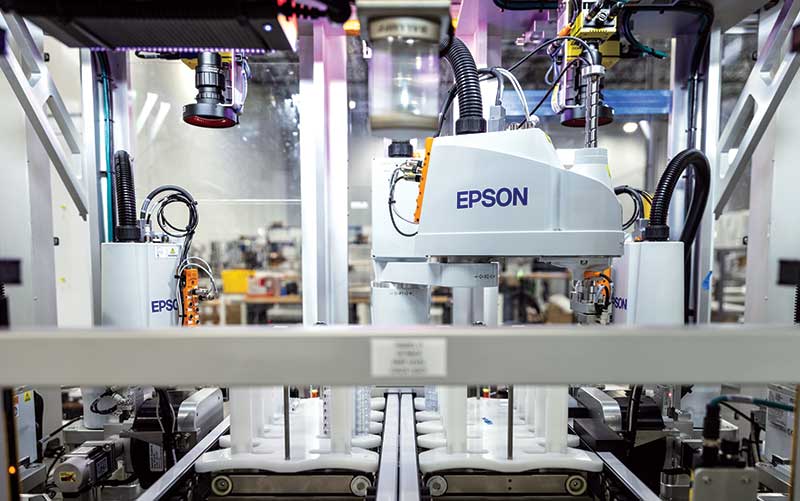

Automated inspection plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing by helping companies improve product quality, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency. As part of our comprehensive robotic automation integration and assembly solutions, we can design automated inspection systems to perform a wide range of tasks, including dimensional and/or surface inspection, defect detection, and quality control.
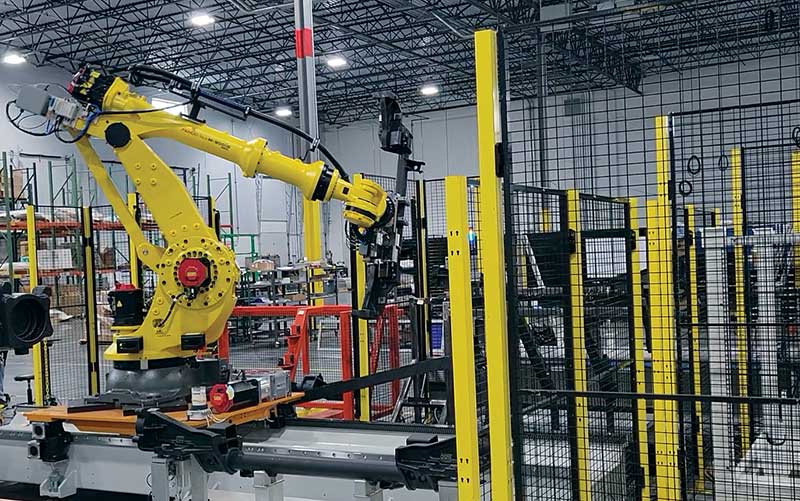

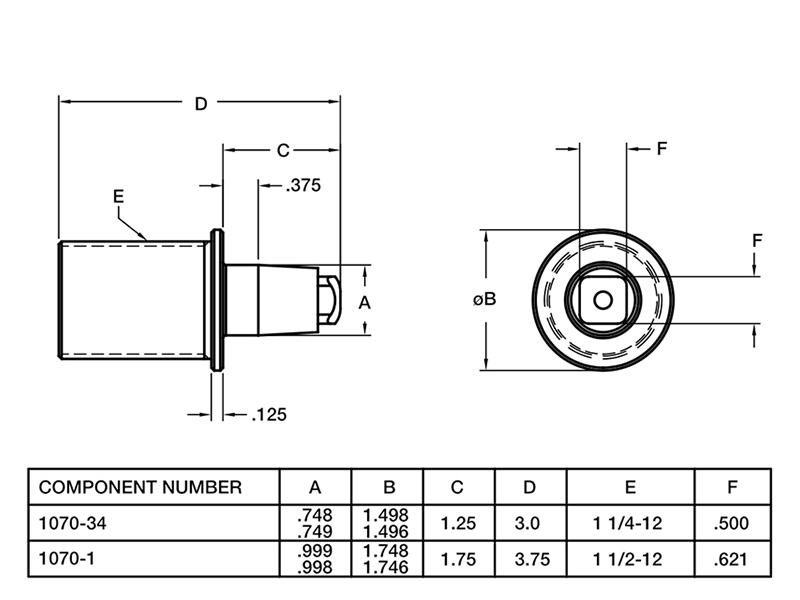
With experience in advanced technologies such as robotics and conveyor belts, we can help manufacturers seamlessly move materials from one station to another as part of our comprehensive robotic automation integration and assembly solutions, streamlining workflows and optimizing resources effectively. Automated material handling systems can also help companies minimize errors or damage during transportation, ensuring that products are handled with precision and care. These systems can be paired with modular tooling solutions, such as the Segen Quick Change system, to reduce downtime and improve overall system efficiency.
Knowledgeable across a variety of joining technologies, Tooling Tech Group is experienced in developing fixtures and automated work cells for the joining of plastic, composite and metal structures. Our innovative, high-quality joining solutions bring efficiency to the shop floor and are designed and built to meet specific customer parts and requirements.
In the realm of post-composite molding, trimming plays a vital role in ensuring that the final product meets all specifications and requirements set forth by designers and engineers. Tooling Tech Group provides precision trimming systems that remove any excess material from the composite part to achieve precise dimensions and smooth edges. These systems, which vary from manual to robot-tended, are designed and built to meet specific customer parts and requirements and may use one or more of the processes below.
Many molded products require the insertion of additional parts to complete the assembly. A snap-fit assembly method creates interlocking features allowing plastic components to “snap” into place precisely. Tooling Tech Group has vast experience in automating this process with a snap press that pushes the multiple parts together to create a strong joint without the need for additional tools or fasteners.
Punch Presses apply precision knockouts of material in a given part, such as is prevalent in bumper facias to accommodate today’s Advanced Drive Assistance Systems (ADAS) sensors.
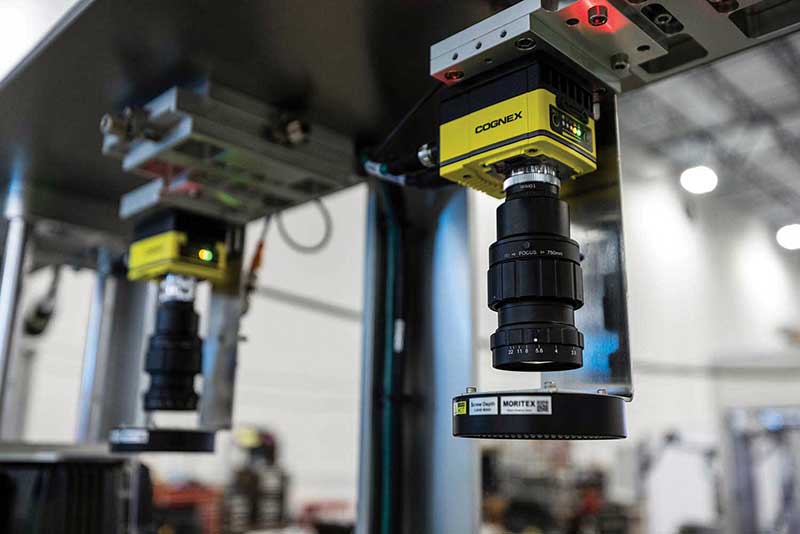

To ensure quality control of the components being manufactured, we can also provide automated vision guidance and monitoring. This cutting-edge technology utilizes cameras and sensors to provide real-time information about processes or activities. It allows for the automatic detection of objects, patterns, or anomalies in images or videos, which helps make informed decisions quickly and allows for pre-determined corrective actions within the software.
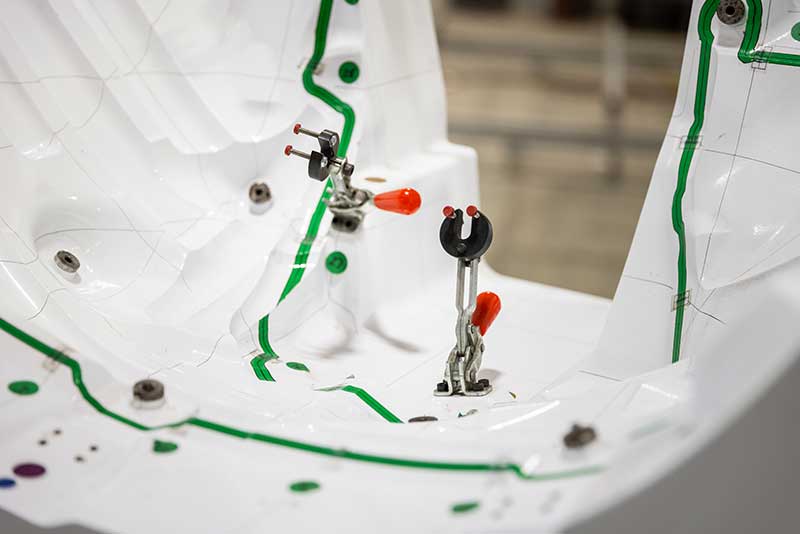
Designed to hold and support parts during inspection, these fixtures allow technicians to easily assess key features such as dimensions, surface finish, and overall integrity. This helps to quickly identify any defects or irregularities in the formed parts before they reach the final assembly stage.

Fill out the form for more information and we will get back to you.